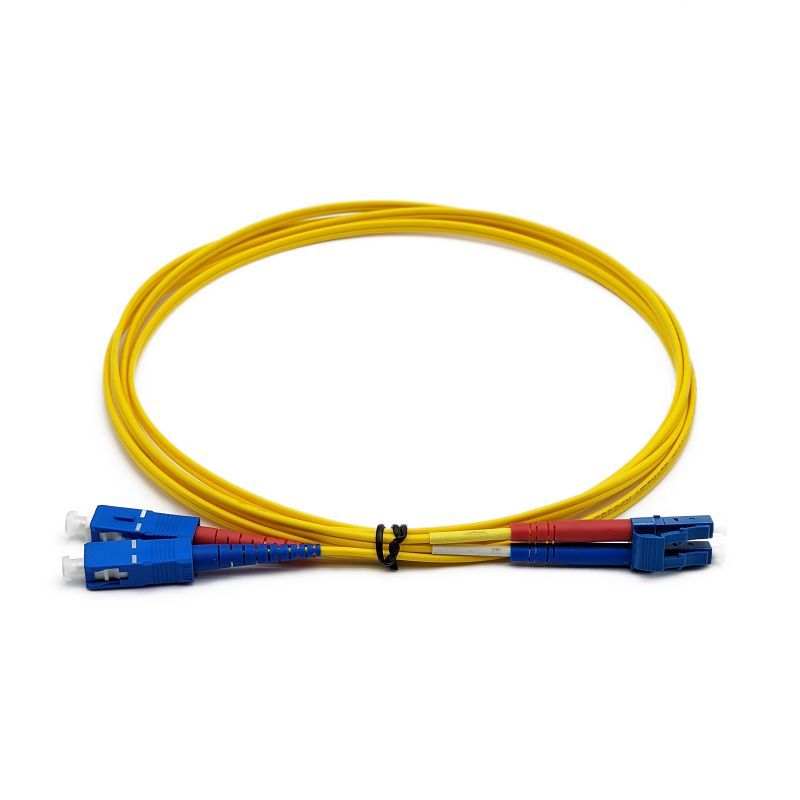
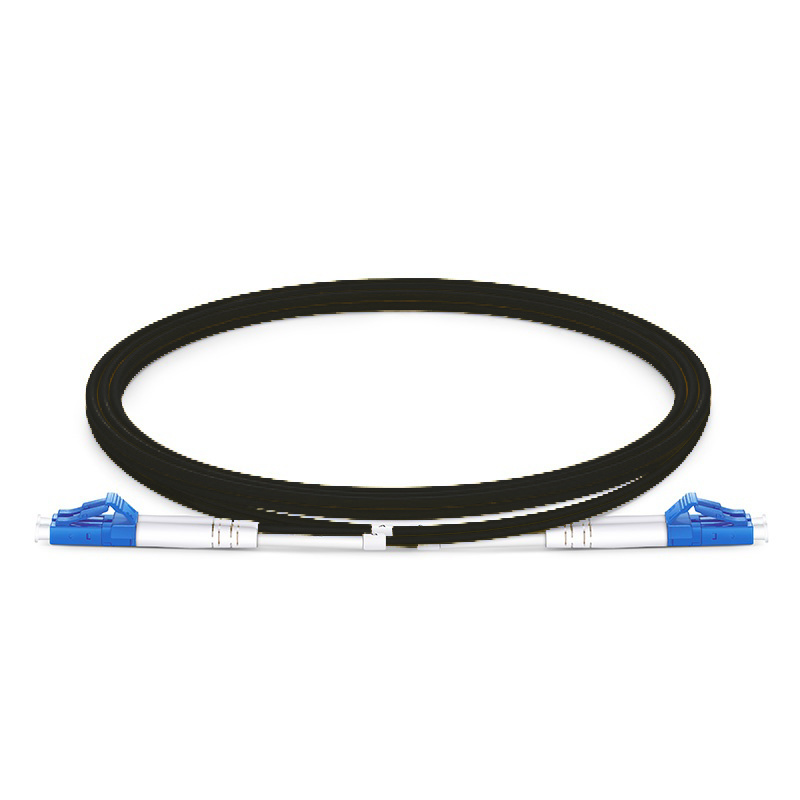
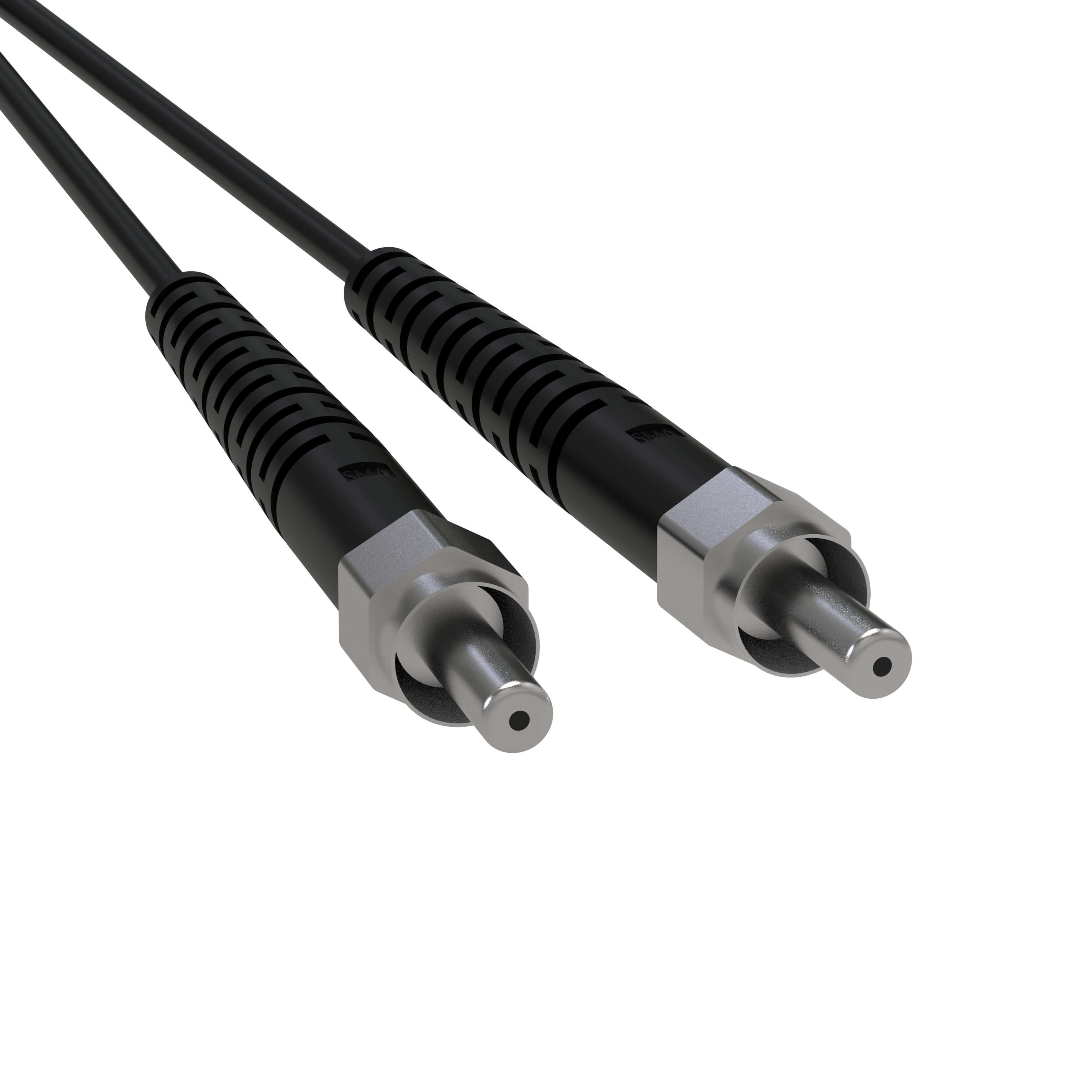
Fiber Patch Cables – High-Performance, Reliable, and Versatile for Networking, Data Centers, and Telecom Applications
Fiber Patch Cables – High-speed, reliable, and low-loss connectors for networking, telecom, and data centers. Available in various lengths and connector types.
2025-12
Fiber patch cables, also known as optical fiber patch cords, are essential components in modern networking and telecommunication systems. These cables are designed to provide high-speed, low-loss data transmission over long distances, making them an ideal choice for a variety of applications, including data centers, telecom infrastructure, and high-performance networks. The use of fiber optics technology has become increasingly important due to its ability to transmit data with minimal signal degradation, superior bandwidth, and high-speed capabilities, which are essential for meeting the demands of today’s digital world.
One of the primary advantages of fiber patch cables is their ability to support high-speed data transmission. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optics use light signals to carry data, allowing them to transmit information at significantly higher speeds. Fiber patch cables are capable of supporting data rates of 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, or even 100 Gbps, depending on the type of fiber and connectors used. This makes them ideal for applications in data centers, high-performance computing environments, and telecom networks that require fast, efficient data transmission with low latency.
Fiber optic technology offers several advantages over traditional copper-based cables, including significantly higher bandwidth, longer transmission distances, and lower signal loss. The use of fiber optics eliminates the risk of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which are common issues with copper cables. This ensures that fiber patch cables provide a clean and stable signal, even in environments with heavy electronic equipment or other sources of interference.
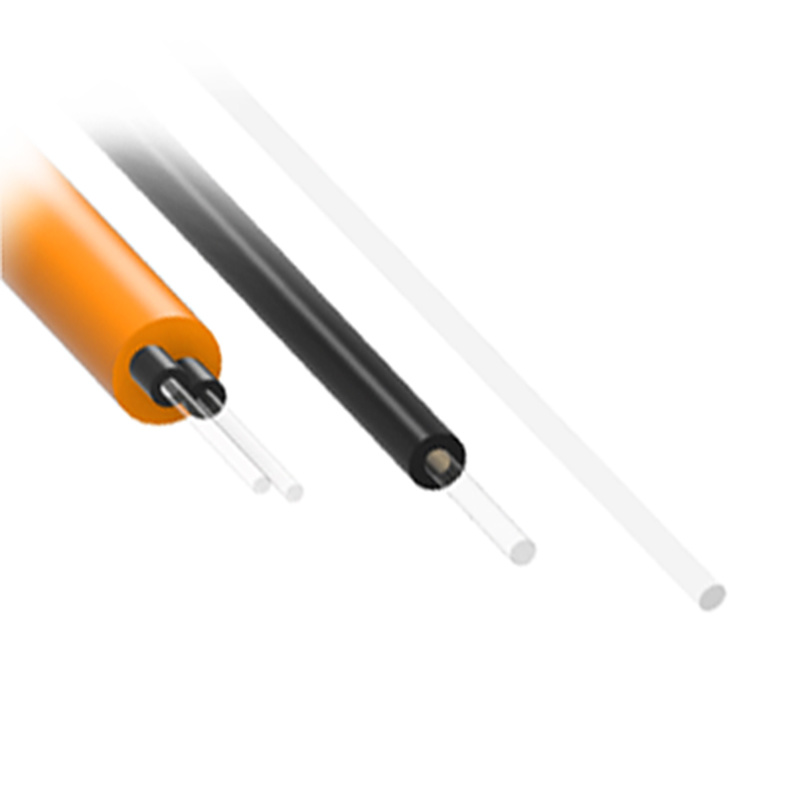
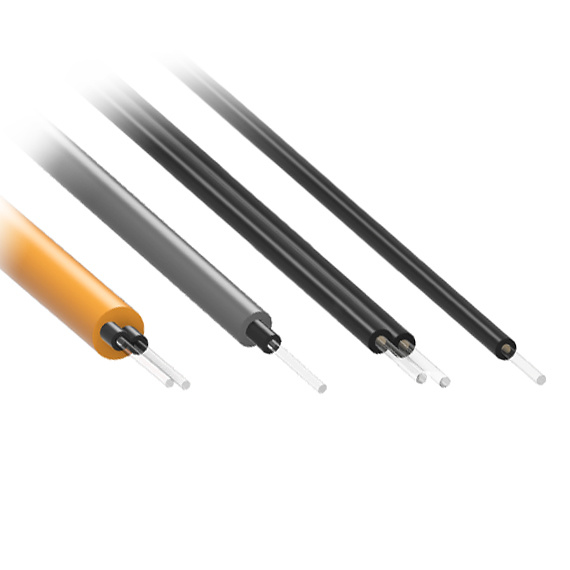
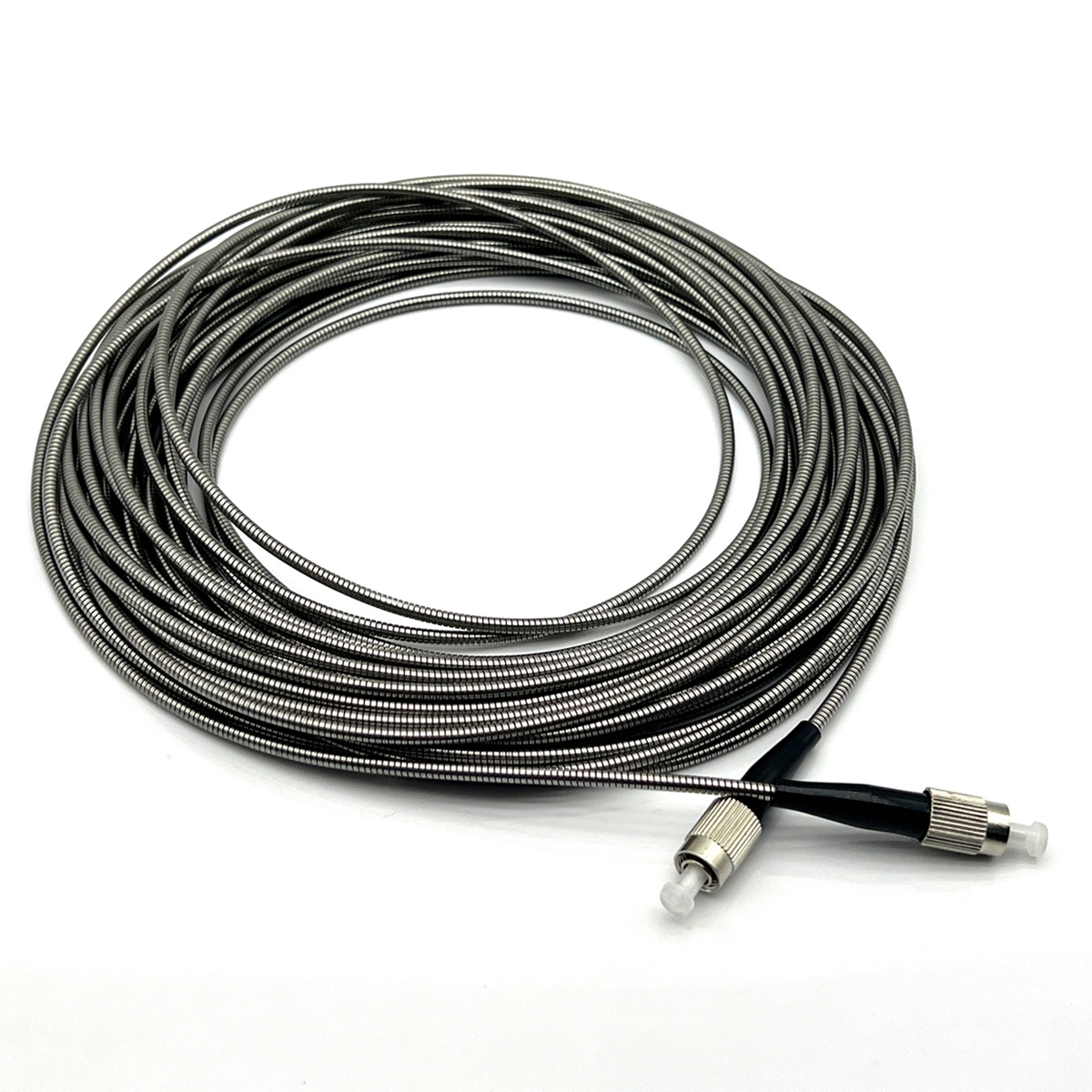
Fiber patch cables are designed to minimize signal attenuation, allowing data to travel longer distances with minimal degradation. This feature is crucial for networks that need to maintain high performance over large areas, such as in data centers or telecommunications networks. Fiber patch cables are available with various connector types, including LC, SC, ST, MTP, MTRJ, and FC connectors, making them compatible with a wide range of equipment. This allows for flexibility in network design and ensures compatibility with existing infrastructure.
Fiber patch cables are constructed with durable materials that are designed to withstand physical stress, environmental factors, and general wear and tear. With proper handling and installation, fiber patch cables can last for many years, providing reliable performance over their lifespan. The protective jacket and outer layers of the cable help shield the fiber core from damage, ensuring that the cable performs optimally throughout its use.
Unlike copper cables, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference. This ensures that the signal remains unaffected by electrical noise, making fiber patch cables ideal for use in environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference, such as hospitals, manufacturing plants, and broadcast facilities. Fiber patch cables are available in various lengths, making it easy to find the right cable for your specific installation needs. They are designed to be flexible, allowing for easy routing and installation in tight spaces, server racks, or cabinets.
While fiber optic cables may have a higher upfront cost compared to copper cables, they offer significant long-term cost savings. Their ability to transmit data at higher speeds and over longer distances reduces the need for additional network equipment and helps minimize overall network maintenance costs. Additionally, fiber patch cables are more energy-efficient, reducing the overall power consumption of the network.
Fiber patch cables are used in a wide variety of applications across different industries. Some common applications include data centers, where fiber patch cables are extensively used to connect servers, switches, routers, and other networking equipment. Their ability to support high-speed data transfer and large amounts of bandwidth makes them essential for managing the increasing data demands of modern cloud computing, big data analytics, and enterprise networks. In telecom networks, fiber patch cables are used to connect transmission equipment and ensure that high-speed internet, voice, and video services can be delivered reliably. Fiber optics are particularly useful in long-distance transmission, as they can cover vast distances without significant signal loss.
Fiber patch cables are used to connect various network components in enterprise environments. Their low latency and high bandwidth capabilities make them ideal for mission-critical applications such as VoIP, video conferencing, and other real-time communication tools that require stable, high-speed data transmission. In the broadcasting and media industry, fiber patch cables are used to connect cameras, audio equipment, and other devices to control rooms and studios. Fiber optics offer the high bandwidth and low latency needed for live broadcasts, ensuring seamless video and audio transmission without interference.
Fiber patch cables are used in industrial environments where electromagnetic interference or harsh conditions might affect traditional copper cables. Their durability and resistance to external interference make them ideal for use in factories, manufacturing facilities, and other industrial settings. There are two primary types of fiber patch cables: single-mode fiber (SMF) and multi-mode fiber (MMF). The choice between these two types of fiber depends on the specific requirements of your network and the distance over which the data needs to be transmitted.
Single-mode fiber is designed for long-distance transmission. It has a small core size (typically 8-10 microns in diameter), which allows light to travel in a single path, reducing signal loss and allowing for higher speeds over greater distances. SMF is commonly used for long-distance communication, such as in telecom networks, long-haul internet connections, and large-scale enterprise networks. Multi-mode fiber has a larger core size (typically 50-62.5 microns in diameter), allowing light to travel in multiple paths. This results in higher signal loss over longer distances compared to single-mode fiber. However, multi-mode fiber is ideal for shorter distance applications, such as in data centers, local area networks (LANs), and enterprise environments.
When selecting fiber patch cables, it is important to consider factors such as the type of network, distance requirements, connector types, and cable performance specifications. Be sure to choose the right fiber optic standard (single-mode or multi-mode) based on the distance over which the data will travel and the type of equipment being used. Additionally, ensure that the cables are compatible with your existing network infrastructure and offer the performance levels required for your specific applications.
In conclusion, fiber patch cables are an essential component in modern networking and telecommunications systems, providing high-speed, reliable, and low-loss data transmission. Their ability to support high bandwidth and long-distance transmission makes them a preferred choice for data centers, telecom networks, and other high-performance applications. With a wide range of connector types, sizes, and configurations available, fiber patch cables offer flexibility and scalability for a variety of installation needs. As the demand for faster, more reliable data transmission continues to grow, fiber patch cables will play an increasingly important role in supporting the infrastructure of the future.
Related News
Sorry,当前栏目暂无内容!
您可以查看其他栏目或返回 首页
Sorry,The current column has no content!
You can view other columns or return Home
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.