Plastic Optical Fiber: Revolutionizing Short-Distance Communication
Meta Description: Discover how Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) is transforming automotive, industrial, medical, and smart home connectivity with its flexibility, EMI resistance, and cost efficiency.
2025-08
Meta Description: Discover how Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) is transforming automotive, industrial, medical, and smart home connectivity with its flexibility, EMI resistance, and cost efficiency.
Introduction
A transparent fiber only 1 mm in diameter is quietly reshaping the way cars, factories, medical devices, and homes stay connected. Beyond the well-known silica glass fiber, another material is gaining traction — Plastic Optical Fiber (POF), a polymer-based fiber designed for short-distance, high-performance data transmission.
Lightweight, highly flexible, and easy to install, POF offers exceptional performance across diverse applications — from luxury car infotainment systems and industrial automation networks to precision medical optics and 8K home theater video links.
1. From Lab to Market: The Development Journey
Research on POF began in the 1960s, when DuPont first used PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) as a fiber core. While early loss rates were high, breakthroughs followed:
1974 – Mitsubishi Rayon (Japan): PMMA/polystyrene core with fluoropolymer cladding, lowering loss to 3500 dB/km.
1990 – Keio University: Development of graded-index (GI) POF with attenuation below 60 dB/km and bandwidth up to 3 GHz.
2000 – Asahi Glass: Fluorinated GI-POF with attenuation of 41 dB/km (850 nm) and 33 dB/km (1300 nm).
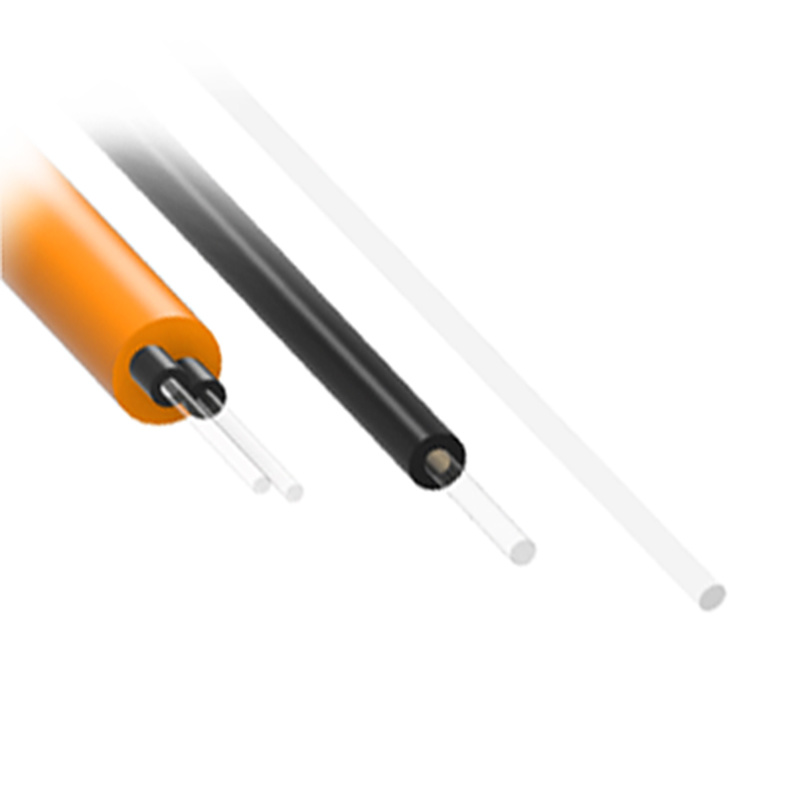
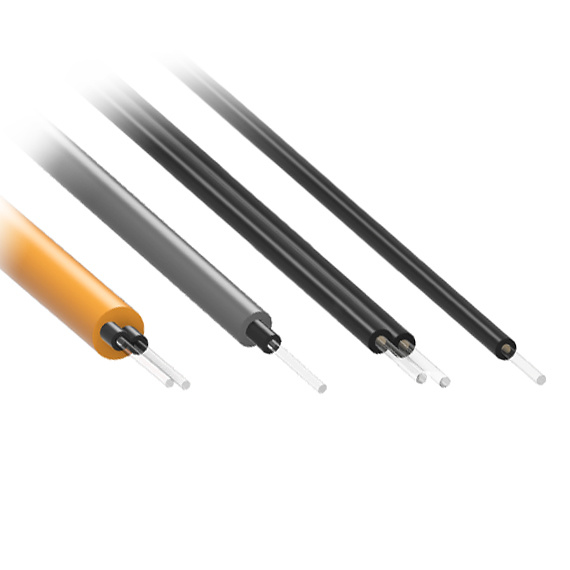
- Materials & Structure: Tailored for Performance
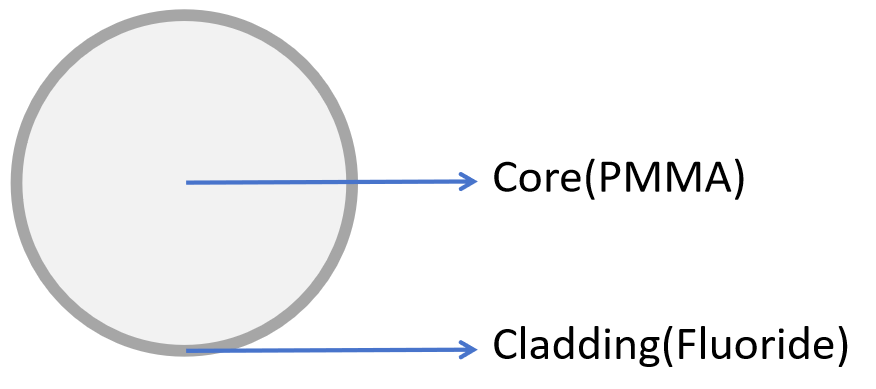
Core Materials
PMMA POF – Low-cost, ideal for 10–100 m at 650 nm (loss ~180 dB/km).
Fluoropolymer POF – Superior for 850–1300 nm, loss 10–50 dB/km, range up to 500 m.
Types of POF
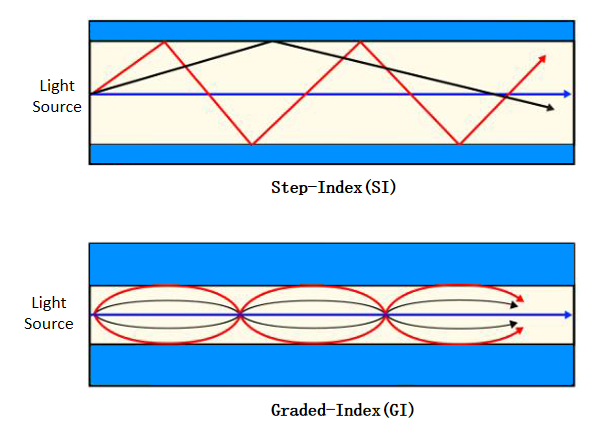
Step-Index (SI-POF): Low-cost, ~5 MHz·km bandwidth; suitable for low-speed, short-range use.
Graded-Index (GI-POF): Bandwidth 1–10 GHz·km; supports gigabit data rates for automotive and industrial networks.
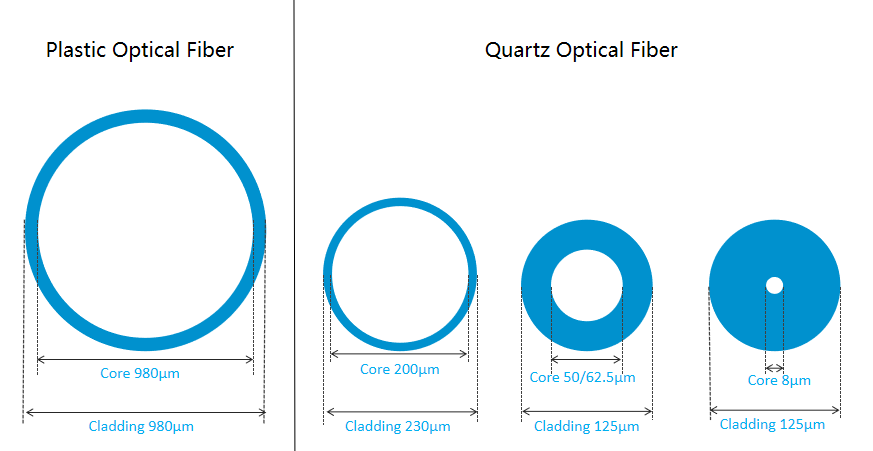
Large core sizes (200–1000 µm) and high numerical aperture provide exceptional alignment tolerance (±30 µm), simplifying installation and reducing costs.
3. Key Advantages of POF
Cost-Effective – Simple polymer drawing process, low energy consumption, scalable for mass deployment.
Flexible & Durable – Bends easily, resists damage even with >1 mm diameter.
Fast Installation – No splicing or polishing required; ready in under a minute.
Excellent EMI Resistance – Thousands of times better than copper in harsh environments.
User-Friendly – Operates at visible 650 nm red light for easy troubleshooting.
4. Application Areas
Automotive Electronics
POF reduces vehicle weight, simplifies wiring, and improves EMI resistance. Common in:
In-vehicle Ethernet (1 Gbps)
Parking assist radar
Infotainment systems
ADAS and sensor networks in EVs and autonomous cars
Industrial Control
Operates from –40 °C to +85 °C, stable in vibration, dust, oil, and chemicals. Ideal for:
Robotics control
Pipeline monitoring
Power system isolation
Integration with RS232, RS422, and 100 Mbps Ethernet
Medical Devices
Non-toxic, soft, and safe — widely used in:
Endoscope light guides
Laser surgical tools
Minimally invasive optical probes
Smart Homes
Slim (≈1 mm), discreetly routed inside walls or moldings, safe from EMI. Perfect for:
Smart lighting control
Home LAN connectivity
IoT device networking
5. Challenges & Future Trends
High transmission loss remains the main challenge:
Traditional PMMA POF: ~100 dB/km at 650 nm
Deuterated PMMA: ~20 dB/km
Perfluorinated polymers: Even lower loss, but costly
Future focus will be on reducing loss and boosting bandwidth. NTT Labs has demonstrated multi-core POF with 1 Tbps capacity for next-generation (6G) networks.
6. Conclusion
With its large-core multimode design, high coupling tolerance, and easy installation, POF offers a reliable and affordable solution for short-distance communications in cars, factories, hospitals, and homes.
As the world moves toward 5G and 6G, POF’s role in edge transmission and low-latency networking will expand. Combined with advances in smart sensing and edge computing, its applications will only grow broader.
From automotive to industrial control, from healthcare to smart living, Plastic Optical Fiber is quietly becoming the backbone of short-range connectivity in the connected world.
Related News
Sorry,当前栏目暂无内容!
您可以查看其他栏目或返回 首页
Sorry,The current column has no content!
You can view other columns or return Home
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.