Fluorescent Fiber Optic Temperature Measurement Principle and Applications
Learn how fluorescent fiber optic temperature sensors work, their advantages, and how Ruiara fiber optic extension cables ensure stable long-distance signal transmission in power and industrial applications.
2025-11
Introduction
Temperature monitoring plays a crucial role in modern power systems, industrial automation, and energy equipment. Traditional electrical sensors often struggle in environments with high voltage, strong electromagnetic interference, or limited access space.
Fluorescent fiber optic temperature sensing technology offers a safe, accurate, and interference-free solution — transmitting optical signals instead of electrical ones. This article explains the principle, system structure, technical advantages, and key applications of fluorescent fiber optic temperature sensors.
1. Working Principle of Fluorescent Fiber Optic Temperature Sensing
Fluorescent fiber optic temperature measurement is based on the fluorescence lifetime principle.
When a fluorescent material at the fiber probe is excited by a light source (usually a pulsed LED or laser diode), it emits fluorescence that decays over time. The fluorescence decay time (τ) is directly related to the local temperature — as the temperature increases, the decay time becomes shorter.
By analyzing the decay curve or phase delay of the returning fluorescent signal through the fiber, the system calculates the temperature with high accuracy. Because the signal transmission is purely optical, it is immune to electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for high-voltage environments.

2. System Composition
A typical fluorescent fiber optic temperature measurement system consists of the following components:
- Fluorescent Fiber Probe: The sensing part coated or doped with fluorescent material.
- Excitation Source: Usually an LED or LD that emits light to excite the fluorescence.
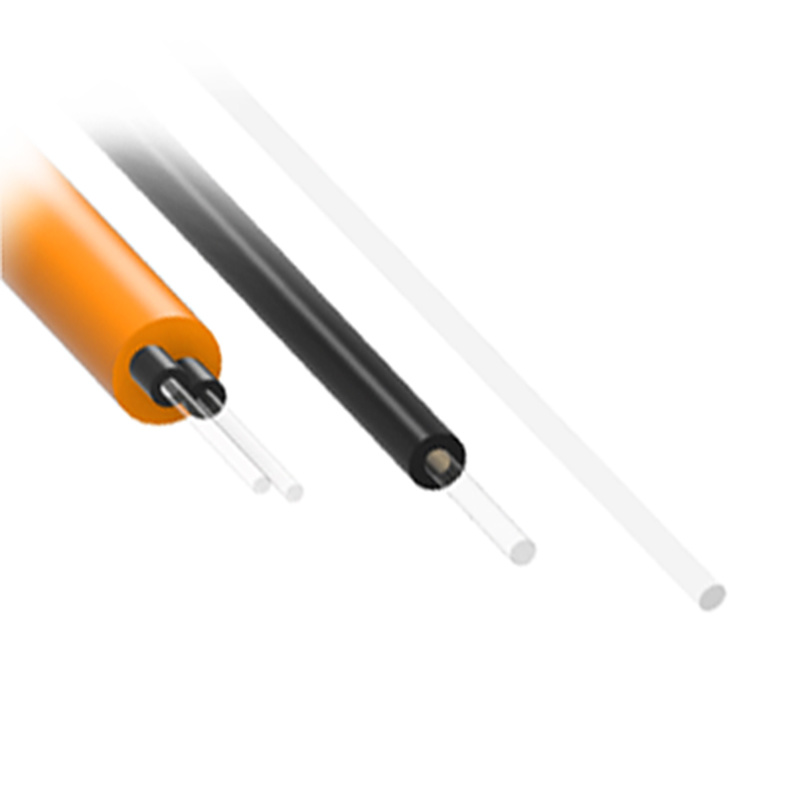
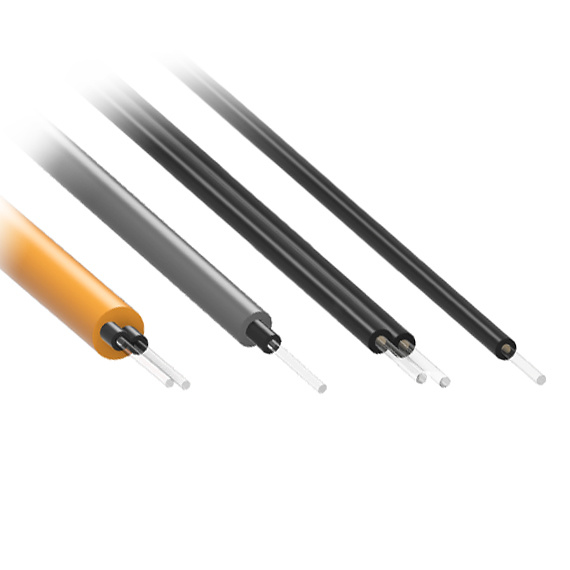
- Optical Fiber Transmission Line: Transmits the excitation and return signals; made from high-quality quartz or plastic optical fiber.
- Detection Module: Converts the returned optical signal into an electrical signal.
- Signal Processing Unit: Calculates the temperature based on the fluorescence lifetime algorithm.

3. Technical Advantages (Highlighting Ruiara Fiber Optic Extension Cables)
Fluorescent fiber optic temperature sensing offers a series of advantages that make it superior to conventional electronic sensors:
- Electromagnetic Immunity
Since optical fibers transmit light rather than electrical current, they are completely immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI). This makes them ideal for high-voltage transformers, switchgear, and power transmission systems. - High Precision and Stability
The fluorescence lifetime principle provides accurate and repeatable temperature readings, unaffected by intensity fluctuations of the light source. - Wide Temperature Range and Fast Response
The sensing probes can operate from −40°C to +250°C (customizable for higher ranges), offering real-time response in dynamic environments. - Safety and Non-Conductive Transmission
Optical fibers are dielectric materials, ensuring complete electrical isolation between the sensing point and the control unit — eliminating the risk of short circuits or ground loops.
Extended Transmission Distance with Ruiara Fiber Optic Extension Cables
In large-scale monitoring systems, sensors may need to be installed far from the detection unit.
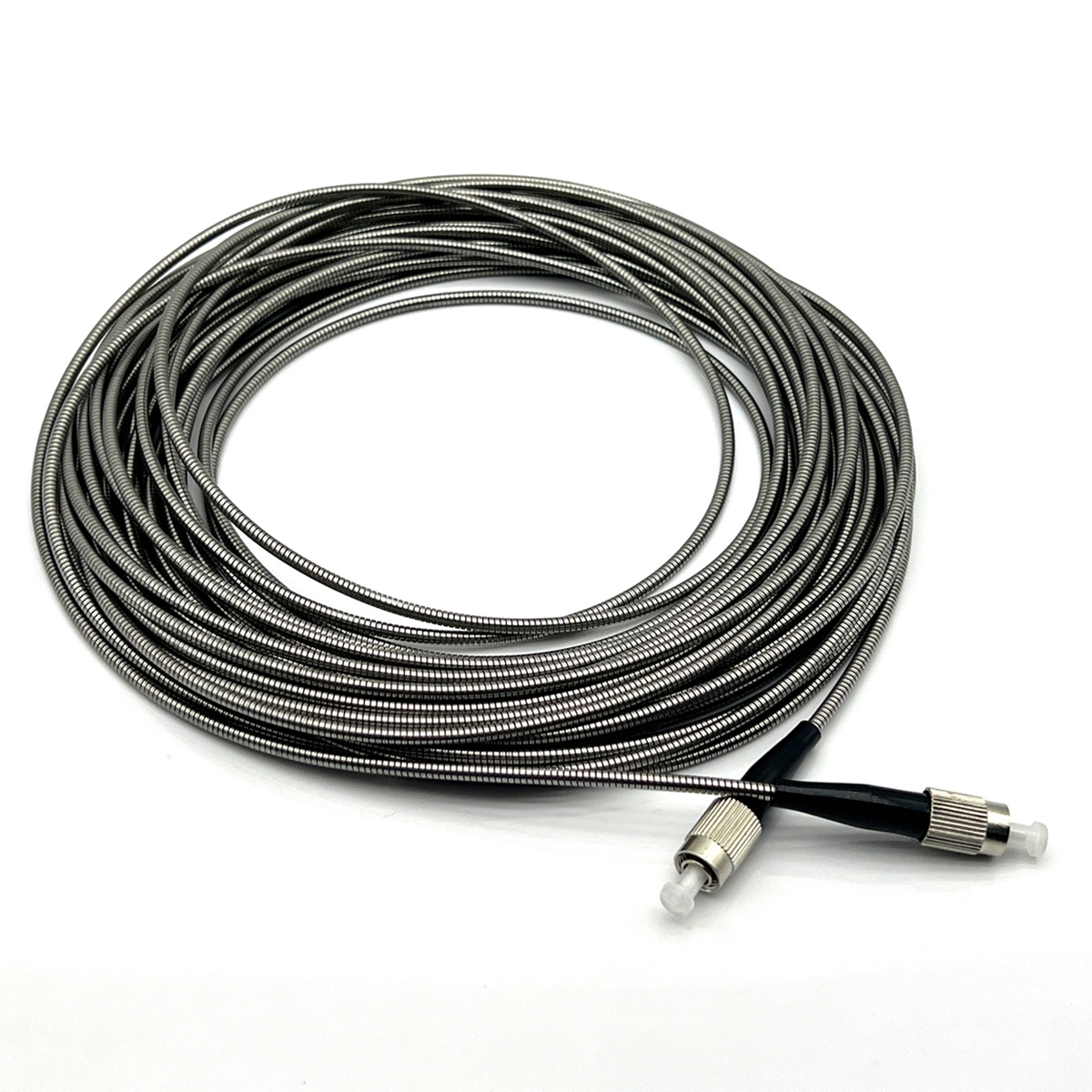
Ruiara’s fiber optic extension cables ensure low-loss, long-distance signal transmission between the fluorescent probe and the temperature analyzer.
These extension cables are available in quartz or plastic optical fiber types, featuring:
- High optical transparency and low attenuation;
- LSZH or armored jackets for outdoor and industrial environments;
- Precise FC/ST/SMA connectors for stable coupling.
This allows users to extend the sensing range up to several hundred meters without affecting measurement accuracy, significantly improving system flexibility and reliability.
4. Typical Applications
(1) Transformer Winding Temperature Monitoring
Used for real-time monitoring of the temperature inside transformer windings to prevent overheating and insulation degradation.
(2) Switchgear and Busbar Temperature Detection
Ensures stable operation of high-voltage cabinets and power distribution systems under heavy load conditions.
(3) Motor and Generator Temperature Monitoring
Monitors stator and rotor temperatures to prevent thermal damage and improve efficiency.
(4) Wind Power and New Energy Systems
Provides distributed temperature monitoring in nacelles, converters, and energy storage systems.
(5) Laboratory and Medical Equipment
Used for precise, non-contact temperature measurements in instruments and biomedical applications.
5. Future Prospects
With the rapid development of smart grids and industrial IoT, fluorescent fiber optic temperature sensing is expected to become a key technology for intelligent condition monitoring.
By combining multi-channel data acquisition and optical fiber networking, it enables comprehensive temperature supervision across complex equipment systems.
Ruiara will continue to develop high-performance fiber optic extension cables and custom sensing assemblies, providing reliable solutions for power, automation, and intelligent monitoring industries.
Related News
Sorry,当前栏目暂无内容!
您可以查看其他栏目或返回 首页
Sorry,The current column has no content!
You can view other columns or return Home
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.